Car Hood Safety Standards: UN ECE R127, FMVSS Rules, and Latch Tests
Modern vehicle hoods aren't just sheet metal covers — they're engineered safety systems designed to protect both occupants and pedestrians. Understanding the regulations that govern hood design reveals the precise engineering requirements manufacturers must meet.
This article documents the specific test procedures, performance criteria, and regulatory timelines for pedestrian head protection and hood latch systems worldwide.
UN ECE Regulation No. 127: The Global Standard
UN Regulation No. 127 on pedestrian safety establishes the principal international requirements for hood (bonnet) surfaces and leading edges. Adopted by the World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations, R127 applies to:
- • M1 vehicles: Passenger cars
- • N1 vehicles: Light commercial vehicles
Regulatory Timeline
The regulation has evolved through multiple series:
- • Series 00: Entry into force 4 February 2015
- • Series 02: Effective 23 May 2018
- • Series 03: Published 21 February 2023
Series 03 Implementation Dates
- • New vehicle types: Mandatory from 7 July 2024
- • All new vehicles: Mandatory from 7 July 2026
The Series 03 update significantly expanded the test area from WAD 2100 mm to WAD 2500 mm and includes windshield testing.
UN R127 Headform Impact Test Specifications
The regulation prescribes detailed headform impact tests to assess potential head injury risk. According to the official UN ECE R127 documentation:
Impact Parameters
- • Impact velocity: 9.7 m/s ± 0.2 m/s (approximately 35 km/h)
- • Impact angle: 50° ± 2° from horizontal
Headform Impactor Specifications
- • Child headform: 3.5 kg mass (represents 6-year-old child)
- • Adult headform: 4.5 kg mass (represents 50th percentile adult male)
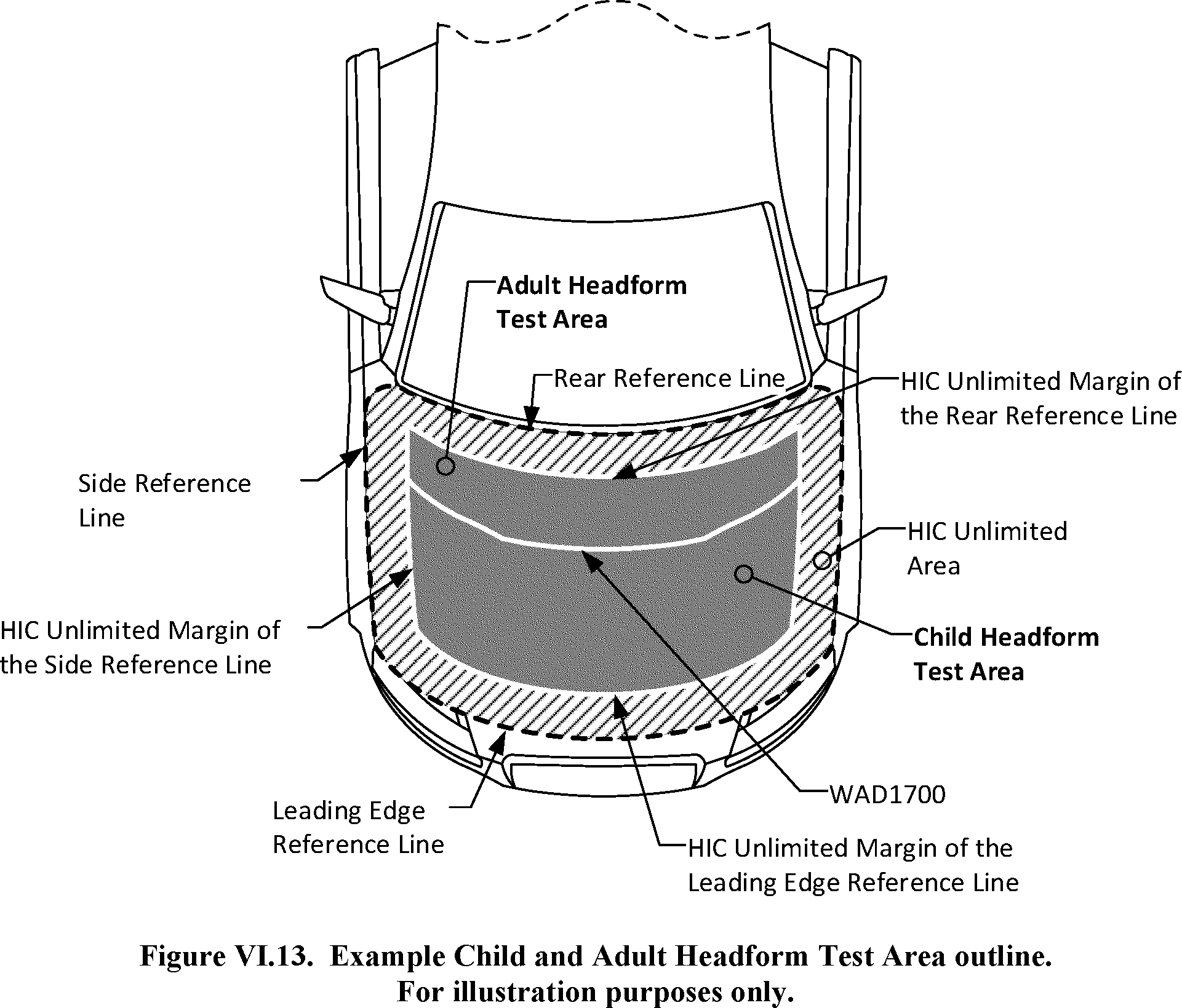
Test Zone Definitions
- • Child headform test area: WAD up to 1,700 mm from ground reference
- • Adult headform test area: WAD 1,700 mm to 2,100 mm (extended to 2,500 mm in Series 03)
- • Minimum spacing between measurement points: 165 mm
- • Minimum tests required: 9 tests per impactor type (3 per third of zone)
HIC Performance Criteria
The Head Injury Criterion (HIC) is the primary pass/fail metric for pedestrian head protection:
HIC Limits by Zone
- • HIC1000 Zone: HIC ≤ 1,000 required on minimum 2/3 of the combined test area (hood + windshield)
- • HIC1700 Zone: HIC ≤ 1,700 permitted for remaining zones (typically edges and structural areas)
What HIC Measures
HIC calculates the probability of head injury based on:
- • Peak resultant acceleration during impact
- • Duration of acceleration pulse
- • Integration of acceleration over the critical time interval
A HIC value of 1,000 corresponds to approximately 18% probability of severe head injury (AIS 4+), while HIC 1,700 represents significantly higher risk — hence its restriction to limited zones.
Bumper (Legform) Test Requirements
UN R127 also specifies lower leg protection tests for the front bumper area:
- • Maximum impact force: ≤ 7.5 kN
- • Maximum bending moment: ≤ 510 Nm
These limits protect against knee ligament damage and tibia fracture in pedestrian impacts.
US Regulation: Proposed FMVSS No. 228
The United States has historically lagged behind international pedestrian protection standards, but NHTSA published a significant rulemaking in 2024.
NPRM Details
According to the Federal Register notice:
- • NPRM published: September 19, 2024 (Federal Register Vol. 89, No. 182)
- • Docket number: NHTSA-2024-0057
- • Comment period: Extended to December 18, 2024
- • Proposed standard: FMVSS No. 228 "Pedestrian Head Protection"
- • Proposed compliance date: First September 1st, two years after final rule publication
Vehicle Categories Covered
The proposed FMVSS 228 would apply to:
- • Passenger cars
- • Light trucks (pickups)
- • Multipurpose passenger vehicles (SUVs, crossovers, vans)
- • Buses with GVWR ≤ 4,536 kg (10,000 lb)
Proposed Test Specifications
- • Child impactor: 3.5 kg (representing 6-year-old head)
- • Adult impactor: 4.5 kg (representing 50th percentile male head)
- • Simulated impact speed: 40 km/h (25 mph)
Proposed Performance Criteria
- • HIC ≤ 1,000: Required on minimum 2/3 of hood test area
- • HIC ≤ 1,700: Permitted for remaining zones
- • Child test zone: WAD up to 1,700 mm
- • Adult test zone: WAD 1,700 mm to 2,100 mm
UN R127 vs. Proposed FMVSS 228: Key Differences
While largely harmonized, some differences exist:
Regulatory Status
- • UN R127: Mandatory in EU, Japan, and other contracting parties since 2015
- • FMVSS 228: Still in NPRM stage as of late 2024 — not yet finalized
Test Area Coverage
- • UN R127 Series 03: Extended to WAD 2,500 mm including windshield
- • FMVSS 228 proposal: WAD up to 2,100 mm (windshield testing not included in initial proposal)
Vehicle Scope
- • UN R127: M1 and N1 categories
- • FMVSS 228: Broader scope including light trucks and buses up to 10,000 lb GVWR
NHTSA Impact Estimates
The Federal Register notice includes NHTSA's safety benefit projections:
- • Estimated lives saved: 67 per year
- • Context: 15% of pedestrian fatalities at 40 km/h involve head-to-hood contact
These estimates justify the compliance costs manufacturers will incur for hood redesigns.
Hood Latch Safety Requirements
Separate from pedestrian protection, hood latch systems must meet retention requirements to prevent unintended opening during vehicle operation.
Basic Requirements
All front-opening hoods that could obstruct driver vision if opened must have:
- • Primary latch: Secures hood in closed position
- • Secondary retention: Either a secondary latch position or separate catch system
Test Criteria
Hood latch systems are typically evaluated to:
- • Resistance to opening under specified inertial loads (g-forces)
- • Dynamic displacement limits without release
- • Endurance cycling (thousands of open/close cycles)
- • Corrosion resistance
Specific test protocols are defined in manufacturer standards and type-approval annexes, with requirements varying by region.
Engineering Implications for Hood Design
Meeting pedestrian protection standards requires specific design approaches:
Structural Considerations
- • Clearance space: Minimum gap between hood outer surface and rigid engine components
- • Deformation zones: Designed crush depth to absorb impact energy
- • Inner panel geometry: Strategic cutouts and weakened sections
- • Active hood systems: Pyrotechnic lifters that raise hood milliseconds before pedestrian contact (used by some manufacturers to achieve HIC targets)
Material Selection
- • Aluminum: Preferred for its deformation characteristics and light weight
- • Composite materials: Increasingly used for tailored energy absorption
- • Steel: Requires more careful inner-structure design to meet HIC limits
Relevance for Aftermarket Modifications
Understanding hood safety standards matters for anyone considering aftermarket hood replacements or modifications. Replacement hoods, carbon fiber upgrades, or hood scoops may affect:
- • Pedestrian protection compliance
- • Latch system compatibility
- • Structural integrity
When planning hood modifications, car visualization platforms like CarCustomizer.io allow you to preview aesthetic changes before purchase — but always verify that aftermarket hoods meet applicable safety requirements for street-legal operation.
Conclusion: Quantified Safety Requirements
Hood safety regulations convert pedestrian protection goals into measurable engineering specifications:
- • UN R127: 3.5/4.5 kg headforms at 9.7 m/s, HIC ≤ 1,000 on 2/3 of test area
- • FMVSS 228: Similar specifications, NPRM published September 2024
- • Legform tests: ≤ 7.5 kN force, ≤ 510 Nm bending moment
- • Latch systems: Primary + secondary retention with specified load resistance
These concrete specifications — impact velocities, impactor masses, HIC thresholds, and compliance dates — represent the engineering reality behind modern hood design. What appears as simple bodywork actually embodies decades of crash research and regulatory development aimed at protecting vulnerable road users.